close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-02-09 Origin: Site








Carrageenan allergy is becoming a growing concern food manufacturers can no longer ignore. As consumers pay closer attention to ingredients, questions around carrageenan sensitivity, respiratory reactions, and clean-label formulations are rising fast. For brands using carrageenan in dairy, beverages, or plant-based products, understanding the risks is now part of responsible product development. This guide explains what carrageenan allergy means, how it differs from intolerance, and what food manufacturers need to know to manage safety, trust, and formulation decisions effectively.
Carrageenan often shows up in food discussions, especially when people talk about reactions. Some call it an allergy. Others say it is a sensitivity. They are not the same, and food professionals should understand the difference.
A carrageenan allergy is a true immune system reaction. It happens when the body treats carrageenan as a harmful substance.
Allergy vs. intolerance
An allergy involves the immune system reacting fast and strongly
An intolerance affects digestion and does not trigger antibodies
How immune reactions differ from inflammation
Allergies are often IgE-mediated, meaning antibodies are involved
Inflammatory responses can happen without IgE or classic allergy markers
It can confuse diagnosis, testing, and consumer communication
| Reaction Type | Immune Involvement | Typical Onset |
|---|---|---|
| True allergy | IgE antibodies | Minutes |
| Sensitivity | Inflammatory | Hours or days |
Clinical research on carrageenan allergy is limited, but it exists. Several case reports describe clear, measurable reactions.
What studies and reports have shown
Controlled exposure triggered immediate symptoms
Lung function dropped shortly after ingestion
Symptoms reversed when carrageenan was removed
Reported immediate reactions
Chest tightness and wheezing
Reduced breathing capacity
Rapid onset after consuming carrageenan-containing foods
These reactions appeared even when other ingredients stayed the same.
Most people who react do not have a classic allergy. They experience carrageenan sensitivity instead.
Non-IgE-mediated reactions
No allergy antibodies detected
Standard allergy tests often come back negative
Symptoms still feel very real to the consumer
Common sensitivity symptoms
Digestive discomfort
Bloating or abdominal pain
Inflammation-related responses
Delayed symptoms appearing hours later
| Aspect | Allergy | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
| Immune antibodies | Yes | No |
| Testing | Sometimes positive | Usually negative |
| Symptoms | Rapid, severe | Delayed, gradual |
This difference matters for labeling, formulation, and consumer trust.
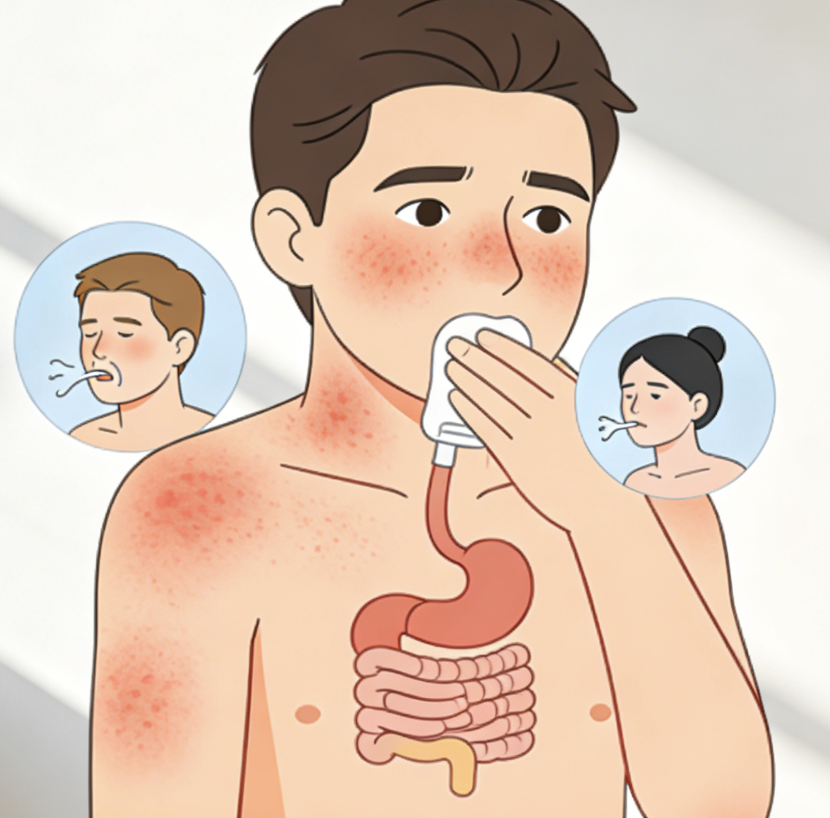
People react to carrageenan in different ways, and the signs are not always obvious at first. Some feel mild discomfort after eating processed foods, while others notice stronger reactions that appear quickly. The response often depends on sensitivity levels, how much is consumed, and existing immune or respiratory conditions.
Mild reactions are easy to overlook because they resemble everyday digestive or throat issues. Chest tightness or a mild pressure sensation may appear, sometimes paired with throat discomfort or irritation while swallowing. These symptoms can feel subtle, yet they often repeat after consuming foods containing carrageenan.
Gastrointestinal symptoms are among the most commonly reported reactions. People may experience stomach cramps, bloating, excess gas, or loose stools. Nausea can also occur, especially after dairy products or plant-based milks where carrageenan is used as a stabilizer.
| Symptom Area | Common Signs | Typical Onset |
|---|---|---|
| Chest | Tightness, pressure | Minutes to hours |
| Digestive | Bloating, cramps, diarrhea | Hours after intake |
In more sensitive individuals, symptoms may appear rapidly and feel more intense. Breathing difficulty, wheezing, or a noticeable reduction in lung function can develop shortly after exposure. These reactions raise concern, especially when they interfere with normal breathing.
Certain populations face higher risks. Children, people managing asthma, and those already sensitive to food additives may react to very small amounts. In these cases, symptoms can escalate faster and require medical attention.
Carrageenan is rarely the only reactive ingredient in processed foods, which makes diagnosis challenging. It often appears alongside dairy proteins, flavoring agents, or preservatives, all of which can trigger similar symptoms.
Dairy is a common confounder because it causes bloating and cramps on its own. Salicylates may contribute to chest tightness or respiratory discomfort, while preservatives can lead to nausea or headaches. Because these ingredients are consumed together, carrageenan reactions are often mistaken for general food intolerance rather than a specific sensitivity.
| Ingredient Type | Overlapping Symptoms | Common Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Dairy proteins | Bloating, stomach pain | Ice cream, yogurt |
| Salicylates | Chest discomfort, wheezing | Flavored drinks |
| Preservatives | Nausea, headache | Packaged meals |
Identifying a carrageenan allergy can feel confusing for patients and clinicians alike. The ingredient hides inside many foods, and reactions often look similar to other intolerances. We usually rely on a combination of clinical tools, symptom tracking, and exclusion methods rather than one single test.
Doctors start by reviewing food history and symptom timing. They look for patterns after consuming processed dairy, plant-based drinks, or packaged foods. Skin testing may be used in some cases, especially when an immediate allergic reaction is suspected. A small amount of carrageenan extract is applied to the skin to check for redness or swelling, although standardized tests remain limited.
Oral food challenges are sometimes used under medical supervision. The patient consumes controlled amounts while clinicians monitor reactions. This method helps confirm cause-and-effect, but it requires caution due to possible respiratory symptoms.
Pulmonary function testing plays a role for patients reporting breathing issues. Changes in FEV1 values can indicate airway involvement after exposure. This approach is especially useful for people managing asthma or chronic respiratory sensitivity.
| Diagnostic Method | What It Evaluates | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Skin testing | Immediate immune response | Suspected acute allergy |
| Oral challenge | Symptom reproduction | Unclear food trigger |
| FEV1 testing | Lung function changes | Wheezing or breathing issues |
Carrageenan allergy often flies under the radar. Routine allergy panels rarely include food additives, so clinicians may not test for it directly. They tend to focus on common allergens like milk, soy, or nuts instead.
Awareness also remains limited. Many consumers assume symptoms come from dairy, preservatives, or general food sensitivity. Some clinicians view carrageenan as harmless fiber, so they may overlook it during diagnosis. Without targeted questioning or elimination trials, the connection often goes unnoticed.
| Common Barrier | Impact on Diagnosis |
|---|---|
| No standard test panels | Additive reactions overlooked |
| Low consumer awareness | Symptoms blamed on other foods |
| Limited clinical training | Inconsi |

Carrageenan may look like a routine stabilizer, yet its perception has shifted fast. Consumers talk more, share faster, and expect brands to respond. We see this pressure most clearly in beverages, dairy, and plant-based products.
Clean-label expectations keep rising. Shoppers read ingredient lists closely and question additives they cannot recognize. They link carrageenan to digestive or breathing discomfort, even when reactions differ person to person. Social media amplifies these concerns. One post spreads quickly, and brands feel the impact long before formal complaints appear.
From a risk standpoint, allergen awareness no longer stays limited to the “big eight.” People now track sensitivities, not just diagnosed allergies. They expect transparency, clear language, and honest explanations.
Manufacturers should ask a simple question first. Do we truly need carrageenan here? In some recipes, it plays a key role in texture or stability. In others, alternative gums or process changes may work just as well.
They also need to watch consumer feedback trends. Digestive complaints, throat irritation, or breathing discomfort reported online often signal sensitivity patterns. Early review helps reduce reformulation costs later.
| Formulation Step | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Ingredient review | Functional need vs. consumer concern |
| Sensitivity monitoring | Feedback, reviews, social platforms |
| Alternative testing | Texture, shelf life, cost impact |
Carrageenan handling deserves the same care as other additives. Shared equipment increases exposure risk, especially in powdered form. Even trace carryover can trigger reactions for sensitive users.
Supplier checks matter too. They should provide clear documentation, consistent specs, and allergen handling procedures. Good records protect brands during audits and help maintain trust across markets.
| Control Area | Practical Action |
|---|---|
| Shared equipment | Dedicated lines or validated cleaning |
| Additive storage | Clear labeling and separation |
| Supplier management | COAs, audits, traceability documentation |
A: For most people, it’s considered safe. Some individuals experience digestive or immune-related reactions, especially those already sensitive to food additives.
A: Rare cases show breathing discomfort or reduced lung function after exposure, mainly in sensitive individuals or children with asthma history.
A: Yes. Food-grade carrageenan differs chemically from degraded forms used in research, which show stronger inflammatory effects.
A: Not always. Brands should weigh functional need, consumer perception, and sensitivity trends before reformulating.
Carrageenan may be a familiar ingredient, yet its impact varies widely across consumers and applications. For food manufacturers, awareness goes beyond compliance. It shapes formulation choices, risk control, and brand credibility in an increasingly allergen-aware market. Paying attention to sensitivity trends early often saves time, cost, and reputation later.
At Megafood (Shanghai) Health Technological Co., Ltd., we support manufacturers navigating ingredient challenges through science-based insight and practical solutions. If you’re exploring reformulation, clean-label strategies, or alternative systems, our team is ready to help you move forward with confidence.
Pneumatic pouring test machine is a new pouring equipment used in the development of laboratory confectionery. The working power of the machine is compressed air, and the whole working environment is hygienic and clean, which meets the production requirements of food hygiene. The machine is controlled by human pneumatic, touch screen operation, compact structure, stable performance. It is an ideal experimental equipment for pouring gelatin, pectin and carrageenan gummy candies.
Information
+86-21-64883956
+86-13916430454
Copyright ©️ Megafood ( Shanghai ) Health Technological Co. , Ltd Technology by leadong.com
